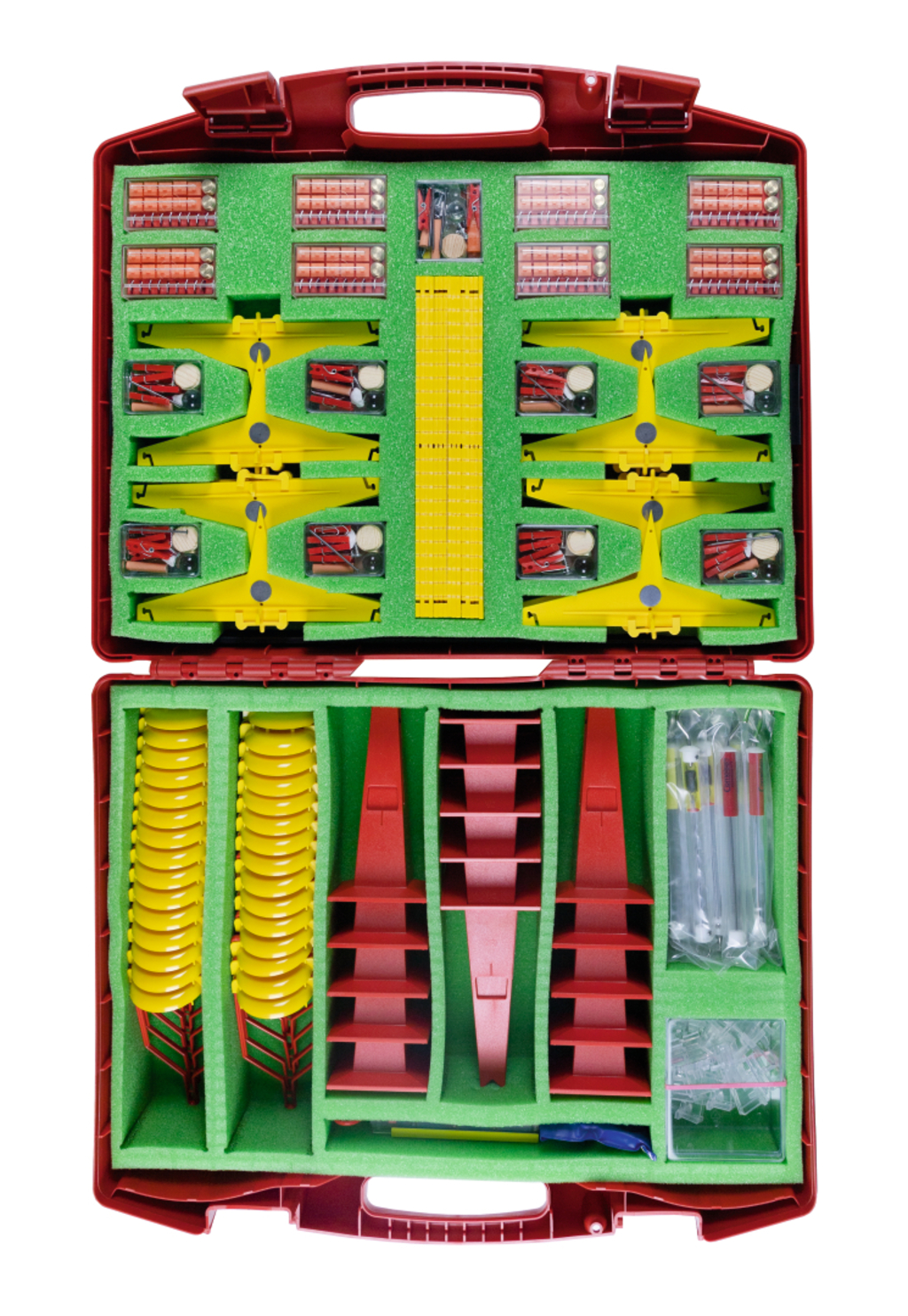
Students kit Balances and equilibrium
The kit provides simple seesaws, beam balances, spring balances, dial balances and balance beam (lever) calculating machines.
Children learn some historical and physical aspects of scales and weighing. They also learn
- to understand the principle of a seesaw
- to assemble and use a beam balance
- to calculate with a system of measures
- a common system of measures
- to appreciate the advantages of a common
system of measures
Age 7-9
Materials for 15 work groups (for 30 children)
Technical specifications
Size of kit: 540 x 450 x 150 mm
The students should deal with the set of weights practically and mathematically.
The students determine the weight of various objects from their school bag. As a learning objective check, they state the weight of some items from the set of small items.
The students should balance various objects (e.g. ruler, pencil, seesaw beam weighted on one side) on their fingers.
The students should understand real playground situations in experiments with the model seesaw and decide how the presented placement problems can be solved.
Using the calculating scales, the students find out in a playful way: The longer the "arm", the fewer weights are needed to balance the beam. The shorter the "arm", the more weights have to be attached. The arm is always the distance from the load - here the weight cube - to the fulcrum (seesaw beam) referred to.
The students use suitable test materials to recreate a Roman scale that is originally shown in two photos. You will find out when you use them: The "arms" of this type of scale are of unequal length. Weights are superfluous once a scale has been established. The weighing is done by establishing the balance with the help of a slider.
The students build a spring scale from prefabricated parts and make a gram scale themselves. The students recognize that if you hang an object on a spring, it expands. The weight of the object can be deduced from the length of its extension.
The students can put together a beam scale from the given individual parts and balance it with the help of the taring slide ("compensating slide").
Through repeated weighing, the students determine any number of pairs of objects from their school materials for which the relationships "heavier than", "lighter than" or "as heavy as" apply.
We will shortly provide you with a description of the experiment at this point.
The students recognize from two drawings: scales have been around for a long time. The forms changed, but the need to determine weights remained the same.
The students learn that the weights in grams and kilograms were not always common and not common among all peoples and that e.g. T. units of weight based on natural resources were used.
We will shortly provide you with a description of the experiment at this point.
The students experience or determine (e.g. in demonstration weighing) the weights of various objects that either occur in their environment or are of particular interest to them.
- 15 × Balance beam, yellow
- 15 × Balance slider (adjustment rider)
- 30 × Scale pan, yellow with red holder
- 15 × Seesaw support
- 13 × Spring scale, 25 g yellow
- 15 × Set of weights (in box)
- 15 × Set of small materials
- 1 × Set of spare parts for balances (in box)
- 1 × Spring balance 5000 g (Graduation: 100 g)
- 1 × Storing diagram,int.vers.
- 1 × Plastic case ca.540x450x150 mm
- 1 × Plastic box 105x90x50 mm
- 15 × Balance stand, plastic red
- 15 × Seesaw, plastic yellow
- 2 × Spring scale, 75 g, red
- 1 × Foam insert 1 for 31780, 505x350x45 mm
- 1 × Foam insert 2 for 31780, 515x360x85 mm
- 1 × Tray 510x360x20 mm